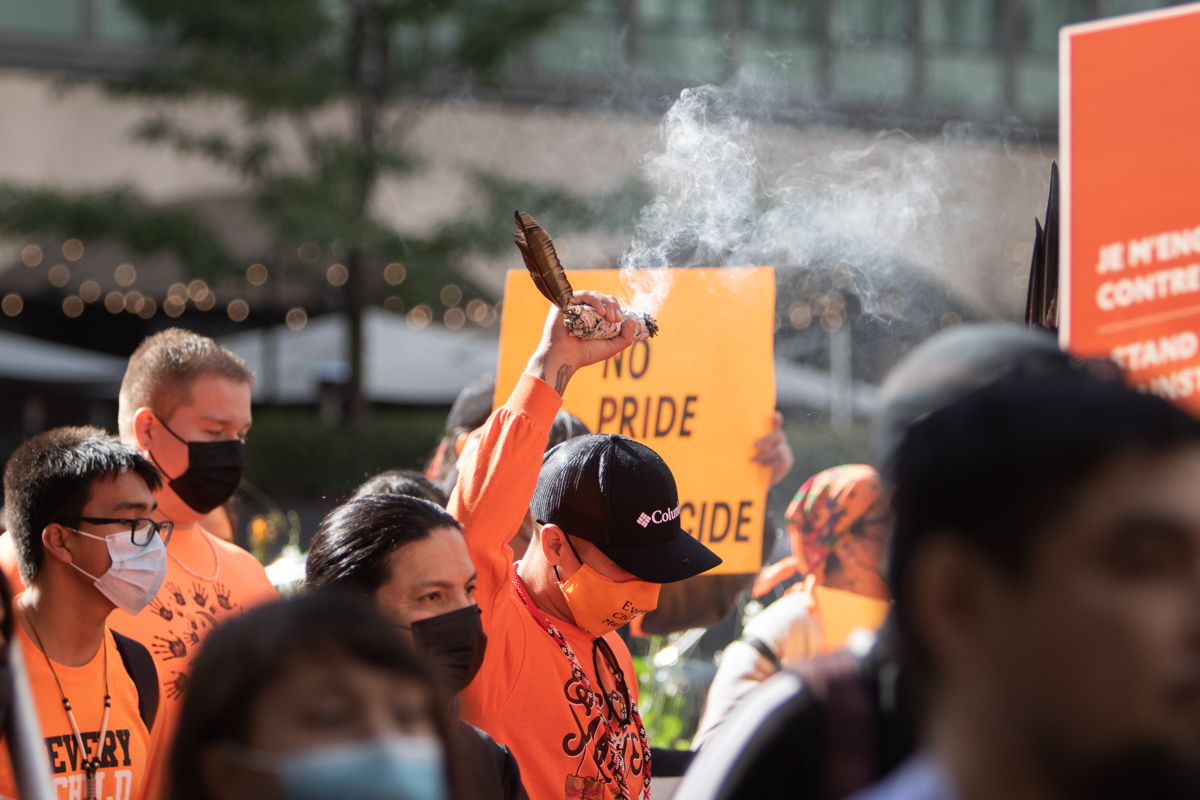Among other communities across Canada, Montreal gathers to mourn and recognize the history of Canada’s residential school system.
On Sept. 30, Indigenous leaders and supporters took it to the streets to mourn the lives of the individuals who died while attending residential schools and those whose bodies may never be found. At the start of the event, ae crowd of hundreds came together at 1 p.m. at Place du Canada near Peel Ave. and René Lévesque Blvd. in front of the former site of the Sir John A. Macdonald statue, to symbolize the genocide orchestrated by the first prime minister, who introduced the residential school system to Canada. Macdonald had a significant role in the creation of the residential school system, and after his statue was torn down by an anonymous group of activists and protestors on Aug. 29, its former site remained a powerful reminder for attendees.
Organized by the Native Women’s Shelter of Montreal (NWSM) and the Assembly of First Nations Quebec-Labrador, the event began with youth from different Quebec and Labrador communities chanting Indigenous traditional music.
To kick off the march, the group witnessed several Indigenous speakers share their stories. As they proceeded to march, the crowd grew to include thousands of people.
Marchers were encouraged to wear orange shirts to stand in solidarity. Orange Shirt Day was started by Phyllis Webstad, a residential school survivor whose orange shirt was taken away from her at the St. Joseph’s Mission residential school in British Columbia. The orange shirt symbolizes how the residential school system took away the identities of Indigenous students, and seeks to honour and remember the experiences and losses of every Indigenous community.
With the recent announcement by Premier François Legault refusing to pass the legislation marking Sept. 30 as a statutory holiday, many voiced their anger. Among the many is Nakuset, executive director of the NWSM.
“I think it’s ridiculous. I think that if you’re going to deny this as a statutory holiday, you’re going to deny us, you’re also denying our existence, you’re denying systemic racism,” said Nakuset.
“Hopefully, when a lot of people show up, we are no longer in denial. This is the day that people have chosen to leave work, to leave school and come be with us, and maybe next year, we’ll change his mind,” she added.
Nakuset emphasized the importance of active reflection.
“The reason why I put this together is because I want this day to be a day of action. I do not want people hanging at home or at work reflecting on this particular day,” she explained. “I think when you come here and listen to speakers, then you actually learn about residential schools,” she continued.
When asked about her hopes and expectations for this march, she insisted on accountability with subpoenas.
“What I [would] like is for people that know about the law to actually start handing out subpoenas for all those residential schools. […] Come to court, share what happened and change the history books, because we need justice,” Nakuset urged.
Though Nakuset sees this holiday as gruesome, she says it is important to remember Sept. 30 as a day of action, a day to learn and a day to do something productive for the future.
Chief Ross Montour of the Mohawk Council of Kahnawà:ke opened his speech by also acknowledging the day as historic.
“We are here to walk today to gather and to remember every life on this day who suffered through the colonization of this country… Those who never came home.”
Montour ended his speech by saying, “I’m happy to be here, but I had to be here.”
Katsi’tsakwas Ellen Gabriel, a Mohawk activist and spokesperson from the Kanehsatà:ke Nation’s Turtle Clan also expressed her thoughts.
“Thank you all for being here […] to support the children of a genocide created by Canada, and the churches that allowed children to be murdered in these residential schools.”
Gabriel continued by mourning the lost lives of all the speakers, the artists, the singers, the musicians, the traditional knowledge keepers, and the medicine keepers that could have been standing with them.
“We are mourning,” she repeated. “We mourn the losses of lives that could have been standing with us.”
“This is our land, and no amount of roses and pavement and policies and lives can change that,” Gabriel added.
She proposed a solution of enforcement of education about Indigenous history in schools. Gabriel addresses this request to the government, and demands a change to educate the youth.
“They tell us our academics can take care of that. Well, education was used as a tool against Indigenous people. Now, we want to use that to turn the tables and use education so you can be assimilated on our terms.”
When discussing the government, Gabriel said the imposed laws are not helpful but rather a form to further oppress them.
“Your laws, they are not for us, they are to oppress us. Your laws, your justice system is to make sure that there is an erasure of Indigenous history in this land that claims to be a human rights defendant.”
Gabriel ended her speech by encouraging everyone to take more action after the demonstration.
“Don’t make this the last thing you do for those children who never came home.”
The speeches ended with a poem addressed to Legault shared by Elisapie, an Inuk singer and songwriter.
Her poem read, “You continue to defend Quebeckers against these accusations of racism from a few individuals, but where are we, the Natives of Quebec, in your speech?”
Photo by Catherine Reynolds.